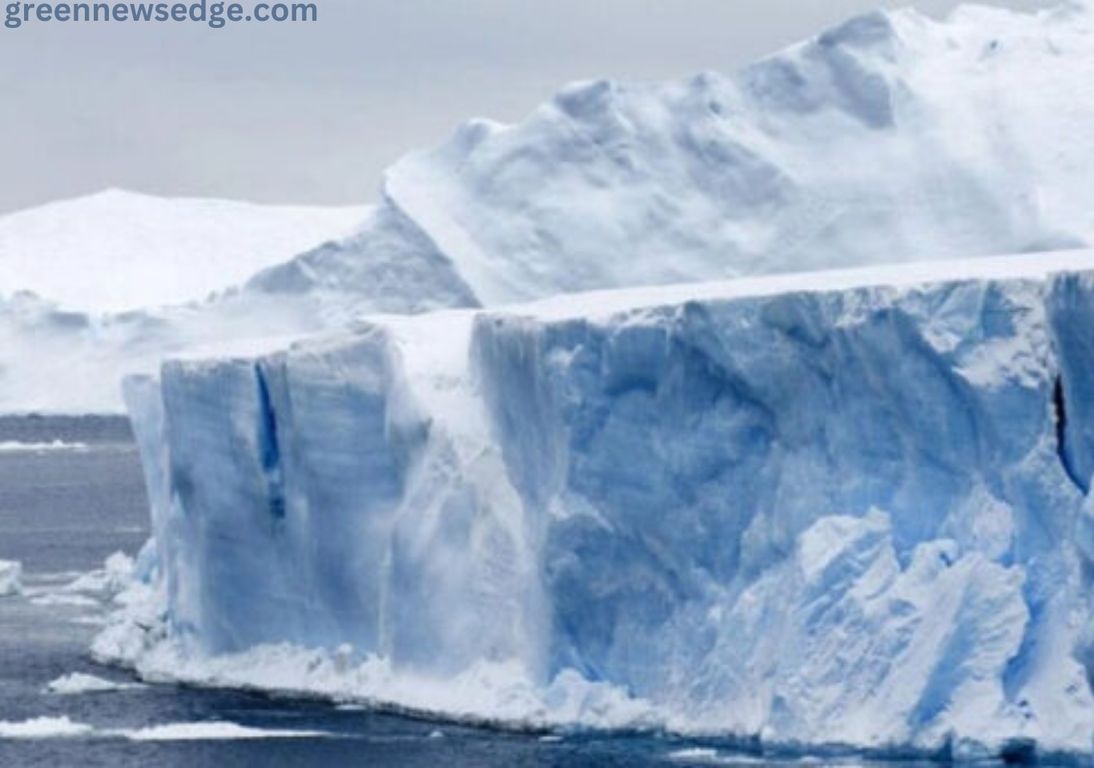
The world’s sea ice has hit an all-time low, sparking concerns about its impact on climate stability. Sea ice, found in the Arctic and Antarctic, acts as a natural cooling system by reflecting solar radiation into space. However, rising global temperatures are causing rapid ice loss, exposing the darker ocean beneath, which absorbs more heat and accelerates warming.
It’s not a distant future problem; it’s happening now. Satellite data shows that the combined extent of Arctic and Antarctic sea ice has reached its lowest recorded levels. This is not a trend we can afford to ignore. The decline is linked to warmer air, rising ocean temperatures, and wind patterns breaking apart the ice. This record drop follows a worrying trend of shrinking sea ice in recent years, highlighting the growing influence of climate change. The time for action is now.
The consequences of this decline are far-reaching. Reduced sea ice affects global weather patterns, disrupts marine ecosystems, and contributes to rising sea levels by destabilizing ice sheets. Scientists warn that continued ice loss could trigger irreversible climate changes. This is not a future possibility, it’s a present danger. It’s essential to monitor and address this alarming trend. As global temperatures continue to rise, urgent efforts are needed to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and protect the planet’s delicate balance. The time for action is now.
Record Low Sea Ice Levels Threaten Climate Stability
The shrinking of Arctic sea ice is a well-documented consequence of climate change. In the 1980s, Arctic sea ice at the end of summer covered an average of 7 million square kilometers. However, by the 2010s, this figure had fallen to just 4.5 million square kilometers, highlighting the dramatic impact of rising global temperatures. The Arctic is warming nearly four times faster than the rest of the world, which accelerates ice melt and alters weather patterns across the globe.
As the bright, reflective ice disappears, the darker ocean beneath absorbs more heat, leading to further warming in a dangerous feedback loop known as ‘albedo feedback ‘. This process not only contributes to rising sea levels but also disrupts marine ecosystems and threatens Indigenous communities that rely on the ice for their way of life. The continued loss of Arctic sea ice has severe implications for global climate stability, as it can weaken ocean currents and increase the frequency of extreme weather events. If greenhouse gas emissions are not reduced, experts predict that the Arctic could experience ice-free summers within the next few decades, leading to even more severe environmental consequences worldwide.
Antarctic Sea Ice Was Once Resilient
Unlike Arctic sea ice, which has been steadily declining for decades, Antarctic sea ice remained relatively stable until the mid-2010s. Scientists were puzzled by its resilience, as climate models predicted that warming temperatures would lead to ice loss in both polar regions. However, since the mid-2010s, Antarctica has experienced a series of record-low sea ice extents, with some years showing a decrease of [specific percentage] compared to the long-term average, signaling a significant shift in its behavior.
Natural variability plays a role in Antarctic ice patterns, as complex oceanic and atmospheric conditions influence the region. However, recent trends suggest that human-induced climate change is now a dominant factor in ice loss. We can’t ignore the role we play in this. As temperatures continue to rise, Antarctic sea ice is becoming increasingly vulnerable. The loss of this ice is particularly concerning because it can contribute to rising sea levels and disrupt global weather systems. The changes in Antarctic sea ice have profound effects on marine life, including krill populations that serve as crucial food sources for whales, seals, and penguins. We need to take responsibility and act now to mitigate these effects.
A Permanent Shift in Antarctic Ice Trends
For years, scientists debated whether the fluctuations in Antarctic sea ice were part of a natural cycle or a sign of long-term change. However, recent data suggests that the region has entered a new phase of consistently lower ice extents. Walter Meier, a senior research scientist at the National Snow and Ice Data Center (NSIDC), has stated that every new data point reinforces the idea that this shift is permanent rather than temporary. Similar to the Arctic, Antarctica now appears to be experiencing an irreversible decline in sea ice.
The reasons behind this shift are complex, but the influence of human-induced climate change is becoming increasingly evident. Rising ocean temperatures, changing wind patterns, and increased heat absorption are all contributing to the loss of Antarctic ice. As the region enters this new regime, scientists fear that continued warming will accelerate the decline even further. The consequences of this shift extend beyond Antarctica itself, as the melting ice influences global sea levels and ocean currents. If the trend continues, coastal communities worldwide could face more frequent flooding and extreme weather events, emphasizing the urgent need for climate action.
Winds, Warm Air, and Ocean Temperatures Driving Ice Loss
Antarctic sea ice is susceptible to external factors such as wind patterns, warm air, and rising ocean temperatures. Unlike the Arctic, which is surrounded by land, Antarctica’s ice is surrounded by ocean, making it more mobile and susceptible to break-up by strong winds. While wind patterns have always played a role in ice movement, scientists now believe that the warming climate is amplifying their effects.
In recent years, unusually warm air masses have contributed to Antarctic ice loss, particularly towards the end of the southern hemisphere’s summer. Higher air temperatures lead to increased surface melting, weakening the ice and making it more prone to breaking apart. Additionally, rising ocean temperatures are melting sea ice from below, further reducing its extent. As these factors combine, they create a vicious cycle of ice loss: warm air leads to surface melting, which weakens the ice and makes it more susceptible to breaking apart, while rising ocean temperatures continue to melt the ice from below. This cycle accelerates ice loss and contributes to the ongoing decline in Antarctic sea ice. Understanding the interplay between these forces is critical for predicting future changes and their impact on global climate systems. Scientists are urging policymakers to take immediate action to mitigate further warming and protect vulnerable polar regions.
Extreme Melting of Antarctic Ice Shelves
The Antarctic ice shelves, massive floating extensions of the continent’s glaciers, have been experiencing extreme levels of surface melting. Unlike sea ice, which forms and melts seasonally, ice shelves are crucial for stabilizing Antarctica’s land-based ice sheets. When these shelves weaken or collapse, they can contribute to rising sea levels by allowing glaciers to flow more rapidly into the ocean.
According to Tom Bracegirdle, a research scientist at the British Antarctic Survey, high air temperatures in December and January created conditions that strongly promoted surface melting. This unprecedented level of melting weakens the structure of ice shelves, making them more prone to breaking apart. Additionally, ongoing ocean warming has created a backdrop that further destabilizes Antarctic ice.
The loss of ice shelves is particularly concerning because it has the potential to trigger cascading effects. As more ice flows into the ocean, sea levels rise, threatening coastal communities worldwide. Scientists are monitoring these changes closely, as the future stability of Antarctica’s ice shelves will play a crucial role in determining the rate of global sea-level rise in the coming decades.
Climate Change’s Role in Record Ice Loss
The dramatic loss of Antarctic sea ice is not just a random occurrence—it is a direct consequence of climate change. A recent study found that the record-low Antarctic sea ice extent in 2023 would have been a one-in-2,000-year event without human-induced warming. However, just two years later, 2025 is on track to surpass that record, highlighting how quickly climate change is reshaping the polar regions.
As greenhouse gas emissions continue to rise, global temperatures are increasing, leading to unprecedented shifts in ice behavior. Scientists warn that the loss of sea ice is not an isolated event but part of a larger pattern of climate instability. The reduction in Antarctic ice contributes to rising sea levels, extreme weather events, and disruptions in ocean circulation, which can affect global climate patterns.
The evidence is clear: without immediate action to reduce carbon emissions and slow global warming, polar ice loss will continue at an accelerated pace. Addressing climate change requires urgent international cooperation, policy changes, and investment in renewable energy to prevent further catastrophic consequences for the planet.
Frequently Asked Questions(FAQ’s)
Why is global sea ice reaching record-low levels?
Global sea ice levels are declining due to rising temperatures caused by climate change. Warmer air and ocean temperatures, along with changing wind patterns, are melting ice in both the Arctic and Antarctic at an unprecedented rate.
How does sea ice loss affect the climate?
Sea ice reflects sunlight, helping to keep the planet cool. When ice melts, the darker ocean absorbs more heat, leading to further warming. This contributes to rising global temperatures, shifting weather patterns, and accelerating ice loss.
Is Arctic sea ice declining faster than Antarctic sea ice?
Historically, Arctic sea ice has declined more consistently. However, in recent years, Antarctic sea ice has also begun to shrink significantly, marking a shift in long-term trends.
What role do wind and ocean currents play in sea ice loss?
Wind patterns can break apart thinner sea ice, making it more vulnerable to melting. Ocean currents carry warm water beneath the ice, further accelerating its decline.
What are the consequences of Antarctic ice loss?
Antarctic ice loss contributes to rising sea levels, destabilizes global ocean currents, and affects marine ecosystems, including species that depend on ice for survival.
Can we stop or slow down sea ice loss?
Reducing greenhouse gas emissions is the most effective way to slow sea ice loss. Transitioning to renewable energy, limiting deforestation, and adopting sustainable practices can help mitigate climate change’s impact.
How does sea ice loss contribute to rising sea levels?
While melting sea ice does not directly raise sea levels, the loss of ice shelves can lead to faster melting of land-based glaciers, which in turn increases sea-level rise.
How does sea ice loss impact wildlife?
Many species, including polar bears, seals, and penguins, rely on sea ice for hunting, breeding, and shelter. The loss of ice disrupts their habitats and threatens their survival.
Conclusion
The record-low levels of global sea ice signal a critical shift in the Earth’s climate system. Arctic sea ice has been steadily declining for decades, and now Antarctic sea ice, once thought to be more resilient, is also reaching unprecedented lows. Scientists warn that this trend is not temporary but a long-term consequence of rising global temperatures driven by climate change.
The loss of sea ice has far-reaching impacts, from accelerating global warming due to reduced solar reflection to disrupting ocean currents and threatening marine ecosystems. Additionally, Antarctic ice shelf melting could contribute to rising sea levels, posing risks to coastal communities worldwide.
Urgent action is needed to address the root causes of ice loss. Reducing greenhouse gas emissions, transitioning to sustainable energy sources, and implementing climate policies are crucial steps in slowing this decline. While natural variability plays a role in sea ice fluctuations, the overwhelming influence of human-induced climate change cannot be ignored.